Types of auto insurance is an essential aspect of responsible car ownership, providing financial protection against various risks and uncertainties on the road. It is a contractual agreement between the policyholder and an insurance company where the policyholder pays regular premiums in exchange for coverage in the event of accidents, theft, or damage to their vehicle. Understanding the types of auto insurance coverage is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring you have adequate protection.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the four primary types of auto insurance coverage: liability, comprehensive, collision, and uninsured/underinsured coverage. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what each type entails and how they can benefit you as a driver.
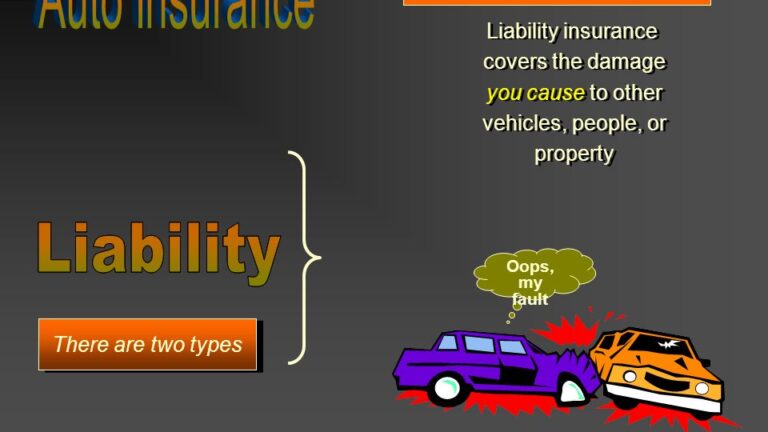
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance is the foundation of auto insurance coverage. It is required in almost every state in the United States and many other countries. The purpose of liability insurance is to protect you financially if you are found responsible for causing an accident that results in bodily injury or property damage to others.
There are two main components of liability insurance:
- Bodily Injury Liability (BI): This portion of your liability insurance covers the medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, and legal fees for injuries sustained by other people in an accident for which you are at fault. It also provides coverage for pain and suffering and lost wages of the injured party. Each state has minimum BI coverage requirements, but it’s often advisable to purchase more than the minimum to ensure adequate protection.
- Property Damage Liability (PD): Property damage liability covers the cost of repairing or replacing the property of others that you damage in an accident. This includes damage to vehicles, buildings, and other structures. Like BI, each state has a minimum requirement for PD coverage.
Liability insurance does not cover your own injuries or property damage; it is solely designed to protect you from financial liability for harming others or their property.
Comprehensive Insurance
Comprehensive insurance, often referred to as “comp,” is an optional coverage that provides protection against non-collision-related damages to your vehicle. While liability insurance covers damage you cause to others, comprehensive insurance covers damage to your own vehicle caused by events other than accidents with other vehicles. These events may include:
- Theft: If your car is stolen, comprehensive coverage will help you recover the value of your vehicle.
- Vandalism: Damage to your vehicle due to malicious acts, such as graffiti or broken windows, is covered under comprehensive insurance.
- Natural Disasters: Comprehensive coverage extends to damage caused by natural disasters like hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, and earthquakes.
- Falling Objects: If a tree branch, rock, or other object falls on your vehicle, comprehensive insurance will cover the repairs.
- Animal Collisions: Comprehensive insurance covers damages resulting from collisions with animals, such as deer or livestock.
- Fire Damage: If your car is damaged or destroyed in a fire, comprehensive coverage will pay for repairs or replacement.
- Glass Damage: Comprehensive insurance covers windshield and glass damage, often with no deductible.
Comprehensive coverage is subject to a deductible, which is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in. The higher the deductible, the lower your premium, but you’ll need to cover more of the repair costs if an incident occurs.
Collision Insurance
Collision insurance is another optional coverage that focuses on damages to your vehicle resulting from collisions with other vehicles, objects, or even when your car flips over. Unlike comprehensive insurance, collision coverage does not cover damages caused by events like theft or natural disasters.
Key points about collision insurance include:
- At-Fault Accidents: Collision coverage is particularly useful if you’re responsible for an accident. It pays for the repairs or replacement of your vehicle, regardless of who is at fault.
- Deductible: Like comprehensive coverage, collision insurance comes with a deductible. You can choose the deductible amount when purchasing your policy.
- New Car Value: If you have a new car, collision coverage can be crucial to protect its value. It typically covers the cost to repair or replace your vehicle up to its actual cash value.
- Older Vehicles: For older cars with lower values, the cost of collision coverage might not be justified. In such cases, some policyholders opt to drop collision coverage to save on premiums.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage is designed to protect you in situations where the at-fault party in an accident either has no insurance (uninsured) or has insufficient coverage to pay for the damages (underinsured). UM/UIM coverage is not mandatory in all states, but it is highly recommended, as it can be a lifesaver in certain scenarios.
Here’s how UM/UIM coverage works:
- Uninsured Motorist (UM) Coverage: If you are involved in an accident with an uninsured driver or if you’re the victim of a hit-and-run, UM coverage can help cover your medical expenses and property damage.
- Underinsured Motorist (UIM) Coverage: UIM coverage comes into play when the at-fault driver’s insurance coverage is insufficient to cover your damages fully. Your UIM coverage will make up the difference, up to the limits specified in your policy.
UM/UIM coverage can be a valuable safety net, especially if you live in an area with a high number of uninsured or underinsured drivers.
Conclusion on types of auto insurance
Auto insurance is a vital component of responsible car ownership, offering financial protection and peace of mind on the road. The four primary types of auto insurance coverage—liability, comprehensive, collision, and uninsured/underinsured coverage—each serve distinct purposes in safeguarding you and your assets.
Liability insurance ensures you can cover the costs if you are at fault in an accident that causes harm to others or their property. Comprehensive insurance protects your vehicle from non-collision-related damages like theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. Collision insurance covers damages resulting from collisions with other vehicles or objects. Lastly, uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage steps in when you encounter drivers with inadequate or no insurance.
To make informed decisions about your auto insurance coverage, it’s essential to assess your individual needs, budget, and the regulations in your state. Ultimately, a well-balanced auto insurance policy provides the security and protection you need while driving in an unpredictable world.